D3D v18.06.12
Development Template
For other 3D printers see 3D Printer Genealogy.
Conceptual Design
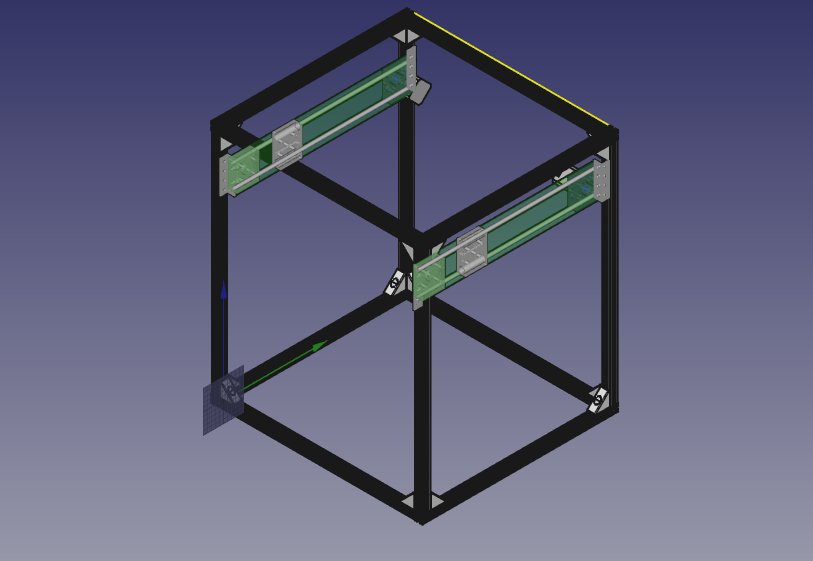
This is a German adaptation of OSE D3D printer. The major differences are:
- It uses T-slot profiles for the frame. It uses preferably parts from UniProKit developed by OSE-Germany.
- It uses metric system.
The remaining parts are similar:
- We use Universal_CNC_Axis.
Optional features:
- Be easier to transport.
- Possibility 1: Use handles as in SolarBox.
- Possibility 2: One should be able to disassemble the printer. The T-Slot profile makes it possible. User:Oliver criticizes this option. It is not useful because time consuming: Disassembling, Assembling, and Calibration.
CAD
For axis orientation I use as reference D3D Ohio v18.02 Universal axis are from [1]. The main difference to OSE-US:
- round edges to prevent warping when made from ABS plastic
- no magnet sockets
BOM
Physics
How fast will be my 3D printer? Can we make it faster? What steppers should I buy?
Traditionally, the knowledge about 3D printer parts, is passed in form of experiment results from older generations of developers. They give good reference points but wee need more flexibility. For example when we build a printer small printer which consumes 200W [2] and a larger printer consumes 400W, does a printer with intermediate dimensions M consumes 300 W? Other interesting questions arise:
- When we want to print twice that fast, do we need stepper motors with twice the torque?
- Can we save energy just by a smart controlling of the printer motion? There is a whole branch in applied mathematics Optimal Control.For other problems see [3].
- Can we learn cool physics from our DIY project 😊?
- Can we learn cool mathematics from our DIY project 😊?
Mechanics
Stepper Motors
I would like to demension stepper motors out of the mechanical properties of 3D printer.
- Stepper Motor
- Stepper Motor Calculations there are only view information.
- Dimensioning of step