The Biochar Economy: Difference between revisions
m (→Specific Products: internal links) |
(various edits, inserted figures) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[Image:2959038953 31a102dc5d.jpg|550px|right]] | [[Image:2959038953 31a102dc5d.jpg|550px|right]] | ||
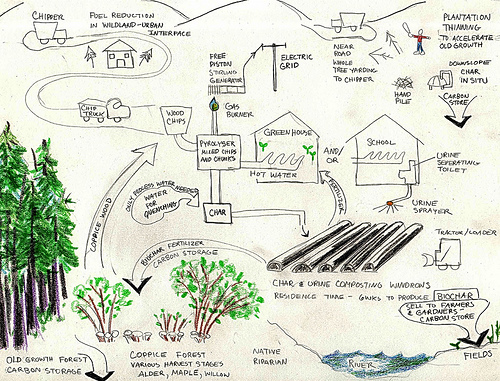
'''Concept:''' Broadly, this refers to various products and processes dealing with [[biochar]], either in its production, transport or end use. Biochar is a carbon-negative product, i.e. its production takes carbon out of the atmosphere and puts it into a form that is stable in soil for a long time. This is an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exothermic exothermic] process: while it does not yield as much energy as full gasification or combustion, it still gives off | '''Concept:''' Broadly, this refers to various products and processes dealing with [[biochar]], either in its production, transport or end use. Biochar is a carbon-negative product, i.e. its production takes carbon out of the atmosphere and puts it into a form that is stable in soil for a long time ("recalcitrant"). This is an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exothermic exothermic] process: while it does not yield as much energy as full gasification or combustion, it still gives off a lot of useful energy. The idea behind the "Biochar Economy" is to try to embed biochar production into other processes (e.g. co-production, see below). This may or may not make economic sense, depending on the market price achievable for biochar and carbon removal from the atmosphere. If the price for biochar and carbon negativity is very low, then this is less efficient and too expensive, considering only the energy yield per unit of biomass. | ||
== | ==Co-Production Concepts== | ||
* [[Biochar/Brick Co-production | |||
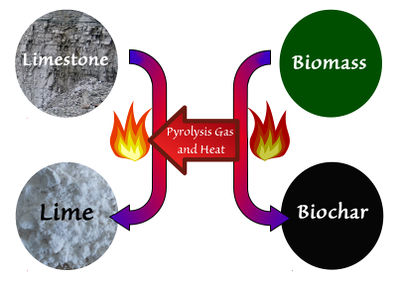
* [[Biochar-Lime Co-production System]] | [[File:Lime Kiln and biochar co-production.jpg|400px|thumb|right|Co-production concept (see [[Biochar-Lime Co-production System|page]]: combination of lime burning and biochar production. Pyrolysis gases from biochar production are captured and burned in the lime [[kiln]], turning limestone into quicklime.]] | ||
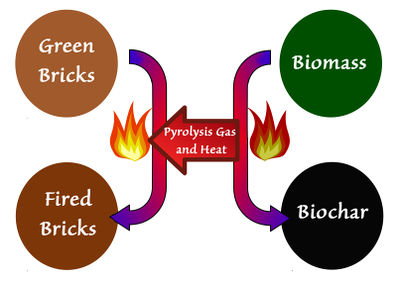
[[File:VSBK mod biochar.jpg|400px|right|thumb|Co-production concept (see [[Biochar/Brick Co-production System|page]]: combination of [[Vertical Shaft Brick Kiln]] and biochar production. Pyrolysis gases from biochar production are captured and used to fire bricks in a VSBK.]] | |||
Co-production can can mean that the energy/heat released during the biochar process is integrated with another process. Examples include: | |||
* [[Direct Reduced Iron|Direct reduced iron]] (iron reduction with pyrolysis gases in a rotary kiln) | |||
* [[Biochar/Brick Co-production System|Biochar/brick co-production system]] | |||
* [[Biochar-Lime Co-production System|Biochar-lime co-production system]] | |||
* [[Biochemicals_from_Pyrolysis|Biochemicals from pyrolysis]] | |||
==Related Products== | |||
* [[Steam_Powered_Wood_Chipper|steam powered wood chipper]] | * [[Steam_Powered_Wood_Chipper|steam powered wood chipper]] | ||
* [[Open_Source_Steam_Weeder|open source steam weeder]] | * [[Open_Source_Steam_Weeder|open source steam weeder]] | ||
* [[The_Charvester_(biochar_producing_tractor)|The "Charvester"]]: a biochar producing tractor | * [[The_Charvester_(biochar_producing_tractor)|The "Charvester"]]: a biochar producing tractor | ||
* steam powered automobile (pyrolysis unit to boil steam) | * steam powered automobile (pyrolysis unit to boil steam) | ||
* [[Aerial_Ropeways#Open_source_ropeway_hardware_for_large-scale_biochar_transport|aerial ropeways]] for efficient biochar transport over long distances | * [[Aerial_Ropeways#Open_source_ropeway_hardware_for_large-scale_biochar_transport|aerial ropeways]] for efficient biochar transport over long distances | ||
==Future Dedicated Wiki== | ==Future Dedicated Wiki== | ||
The number of applications for such a new ecomomy is vast. Therefore, a dedicated wiki is needed. Any interested participants please raise your hands, contact the author of this page (see history tab). | The number of applications for such a new ecomomy is vast. Therefore, a dedicated wiki is needed. Any interested participants please raise your hands, contact the author of this page (see history tab). | ||
Revision as of 14:54, 27 April 2016
Concept: Broadly, this refers to various products and processes dealing with biochar, either in its production, transport or end use. Biochar is a carbon-negative product, i.e. its production takes carbon out of the atmosphere and puts it into a form that is stable in soil for a long time ("recalcitrant"). This is an exothermic process: while it does not yield as much energy as full gasification or combustion, it still gives off a lot of useful energy. The idea behind the "Biochar Economy" is to try to embed biochar production into other processes (e.g. co-production, see below). This may or may not make economic sense, depending on the market price achievable for biochar and carbon removal from the atmosphere. If the price for biochar and carbon negativity is very low, then this is less efficient and too expensive, considering only the energy yield per unit of biomass.
Co-Production Concepts
Co-production can can mean that the energy/heat released during the biochar process is integrated with another process. Examples include:
- Direct reduced iron (iron reduction with pyrolysis gases in a rotary kiln)
- Biochar/brick co-production system
- Biochar-lime co-production system
- Biochemicals from pyrolysis
Related Products
- steam powered wood chipper
- open source steam weeder
- The "Charvester": a biochar producing tractor
- steam powered automobile (pyrolysis unit to boil steam)
- aerial ropeways for efficient biochar transport over long distances
Future Dedicated Wiki
The number of applications for such a new ecomomy is vast. Therefore, a dedicated wiki is needed. Any interested participants please raise your hands, contact the author of this page (see history tab).