Torrefaction: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Added some more links under the "External Links" section) |
m (Minor Typo Fix) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
*Produces mainly [[Tar]] , and [[Charcoal]] | *Produces mainly [[Tar]] , and [[Charcoal]] | ||
*Can clog vents etc if not accounted for in design | *Can clog vents etc if not accounted for in design | ||
*If | *If intentional the calorific value of biomass can be greatly increased | ||
*Benefits are: | *Benefits are: | ||
**Higher energy density | **Higher energy density | ||
**More homogeneous composition | **More homogeneous composition | ||
** | **Hydrophobic behavior | ||
**Elimination of biological activity | **Elimination of biological activity | ||
**Improved grindability. | **Improved grindability. | ||
Revision as of 00:32, 12 April 2022
Basics
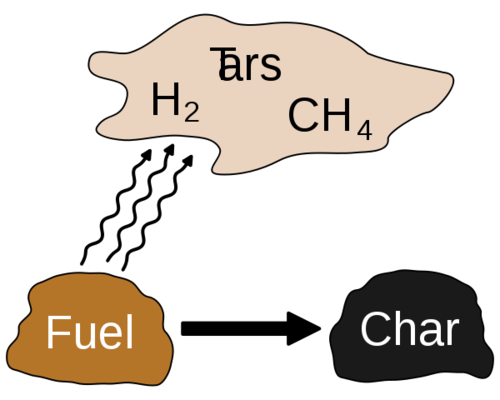
- A mild form of Biomass Pyrolysis at temperatures typically between 200 and 320 °C
- Produces mainly Tar , and Charcoal
- Can clog vents etc if not accounted for in design
- If intentional the calorific value of biomass can be greatly increased
- Benefits are:
- Higher energy density
- More homogeneous composition
- Hydrophobic behavior
- Elimination of biological activity
- Improved grindability.
- Seems to be via coating the resulting char in the tar via it not being extracted/removed in the flue gas?
Internal Links
- Bio-Tar
- Bio-Asphalt
- Wood Preservation by Carbonization
- Pelletized biomass and Wood Chips
- Kon-Tiki Kiln and Biochar
External Links
- The Wikipedia Page on Torrefaction
- An Article by " The Coalition for Sustainable Rail " titled "Torrefied Biomass"