Torrefaction: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
(Updated the page to the more recent formatting style) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Basics= | |||
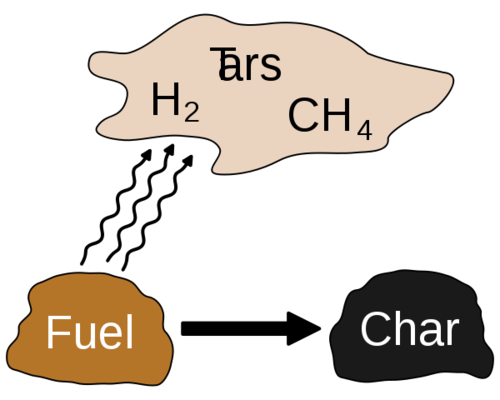
[[File:600px-Pyrolysis.svg.png|thumb|right|500px|Torrefaction removes moisture and some volatiles from wood. Further heating leads to carbonization, which mobilizes more volatiles and changes the properties of some of the constituents (e.g. due to polymerization).]] | [[File:600px-Pyrolysis.svg.png|thumb|right|500px|Torrefaction removes moisture and some volatiles from wood. Further heating leads to carbonization, which mobilizes more volatiles and changes the properties of some of the constituents (e.g. due to polymerization).]] | ||
Torrefaction of biomass, e.g., wood or grain, is a mild form of pyrolysis at temperatures typically between 200 and 320 °C. The calorific value of biomass can be greatly increased by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Torrefaction torrefaction]. Benefits are: higher energy density, more homogeneous composition, hydrophobic behavior, elimination of biological activity, improved grindability. | Torrefaction of biomass, e.g., wood or grain, is a mild form of pyrolysis at temperatures typically between 200 and 320 °C. The calorific value of biomass can be greatly increased by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Torrefaction torrefaction]. Benefits are: higher energy density, more homogeneous composition, hydrophobic behavior, elimination of biological activity, improved grindability. | ||
== | =Internal Links= | ||
* [[Wood Preservation by Carbonization]] | *[[Bio-Tar]] | ||
* [[Pelletized biomass]] and [[Wood Chips]] | *[[Bio-Asphalt]] | ||
* [[Kon-Tiki Kiln]] and [[Biochar]] | *[[Wood Preservation by Carbonization]] | ||
*[[Pelletized biomass]] and [[Wood Chips]] | |||
*[[Kon-Tiki Kiln]] and [[Biochar]] | |||
=External Links= | |||
*[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Torrefaction The Wikipedia Page on Torrefaction] | |||
[[Category:Biofuel]] | [[Category:Biofuel]] | ||
[[Category:Energy]] | [[Category:Energy]] | ||
Revision as of 02:09, 21 June 2020
Basics
Torrefaction of biomass, e.g., wood or grain, is a mild form of pyrolysis at temperatures typically between 200 and 320 °C. The calorific value of biomass can be greatly increased by torrefaction. Benefits are: higher energy density, more homogeneous composition, hydrophobic behavior, elimination of biological activity, improved grindability.
Internal Links
- Bio-Tar
- Bio-Asphalt
- Wood Preservation by Carbonization
- Pelletized biomass and Wood Chips
- Kon-Tiki Kiln and Biochar