Pelletized biomass: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(inserted image gallery) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:WoodPellets01.jpg|500px|thumb|right|Wood pellets are the most common type of pellet fuel and are generally made from compacted sawdust and related industrial wastes from the milling of lumber, manufacture of wood products and furniture, and construction.]] | [[File:WoodPellets01.jpg|500px|thumb|right|Wood pellets are the most common type of pellet fuel and are generally made from compacted sawdust and related industrial wastes from the milling of lumber, manufacture of wood products and furniture, and construction.]] | ||
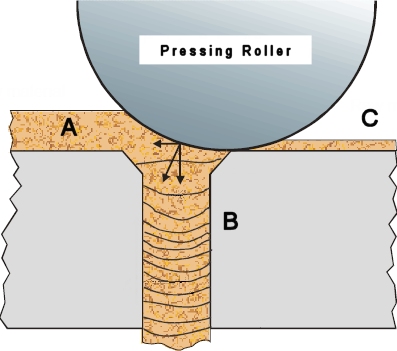
Biomass can be [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pellet_fuel pellitized] by first passing it through a [[Hammer Mill]] for uniformity, then feeding it to a press that has holes of uniform size. In this process, there is a marked increase in temperature, causing the lignin to plastify. | Biomass can be [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pellet_fuel pellitized] by first passing it through a [[Hammer Mill]] for uniformity, then feeding it to a press that has holes of uniform size. In this process, there is a marked increase in temperature, causing the lignin to plastify. General categories of biomass pellets include: industrial waste and co-products, food waste, agricultural residues, energy crops, and virgin lumber. Wood pellets are the most common type of pellet fuel and are generally made from compacted sawdust. | ||
==Elsewhere on OSE Wiki== | The regular geometry and small size of fuel pellets allow automatic feeding with very fine calibration. They can be fed to a burner by auger feeding or by pneumatic conveying. Their high density also permits compact storage and transport over long distance. | ||
[[Pelletizer]], [[Biomass to Fuel]], [[Biofuel]], [[Wood Chips]], [[Gasifier]] | |||
==Torrefaction== | |||
Calorific value can be greatly increased by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Torrefaction torrefaction]. Benefits are: higher energy density, more homogeneous composition, hydrophobic behavior, elimination of biological activity, improved grindability. | |||
==Elsewhere on the OSE Wiki== | |||
* [[Pelletizer]], [[Pelletizer/Research Development]], [[Pelletizer Log]], [[Nick on the Pelletizer]] | |||
* [[Biomass to Fuel]], [[Biofuel]], [[Wood Chips]], [[Gasifier]] | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pelletizing Pelletizing] | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pellet_fuel Pellet fuel] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pelletizing Pelletizing in general] | ||
* Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Torrefaction Torrefaction] | |||
* Biomass Magazine: [http://www.biomassmagazine.com/article.jsp?article_id=2465 "The Art of Biomass Pelletizing"] | * Biomass Magazine: [http://www.biomassmagazine.com/article.jsp?article_id=2465 "The Art of Biomass Pelletizing"] | ||
==Image Gallery== | |||
<div align="left"><gallery widths="400px" heights="400px"> | |||
File:Sawdust.jpg|Sawdust from [[Sawmill]] | |||
File:WoodPellets.jpg|Wood Pellets | |||
File:GrassPellet.jpg|Grass Pellets | |||
File:Pelletizer.jpg|Wood Pelletizer | |||
File:Pelletizer.png|GVCS Pelletizer Mockup | |||
File:rollerdie.jpg|Roller die | |||
</gallery></div> | |||
[[Category:Biofuel]] | [[Category:Biofuel]] | ||
[[Category:Pelletizer]] | |||
[[Category:Farm equipment]] | |||
Revision as of 02:00, 17 August 2016
Biomass can be pellitized by first passing it through a Hammer Mill for uniformity, then feeding it to a press that has holes of uniform size. In this process, there is a marked increase in temperature, causing the lignin to plastify. General categories of biomass pellets include: industrial waste and co-products, food waste, agricultural residues, energy crops, and virgin lumber. Wood pellets are the most common type of pellet fuel and are generally made from compacted sawdust.
The regular geometry and small size of fuel pellets allow automatic feeding with very fine calibration. They can be fed to a burner by auger feeding or by pneumatic conveying. Their high density also permits compact storage and transport over long distance.
Torrefaction
Calorific value can be greatly increased by torrefaction. Benefits are: higher energy density, more homogeneous composition, hydrophobic behavior, elimination of biological activity, improved grindability.
Elsewhere on the OSE Wiki
- Pelletizer, Pelletizer/Research Development, Pelletizer Log, Nick on the Pelletizer
- Biomass to Fuel, Biofuel, Wood Chips, Gasifier
See Also
- Wikipedia: Pellet fuel and Pelletizing in general
- Wikipedia: Torrefaction
- Biomass Magazine: "The Art of Biomass Pelletizing"
Image Gallery
Sawdust from Sawmill