Product Ecologies: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
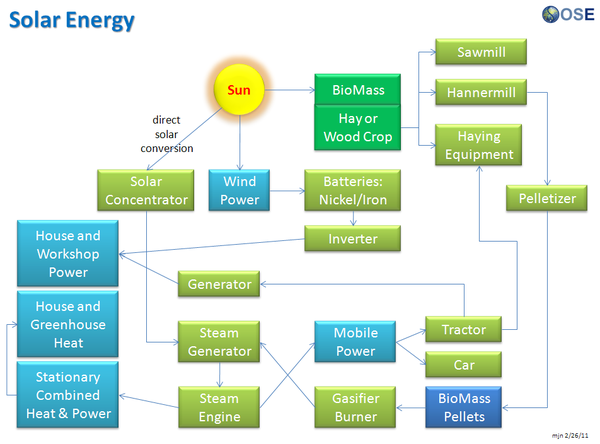
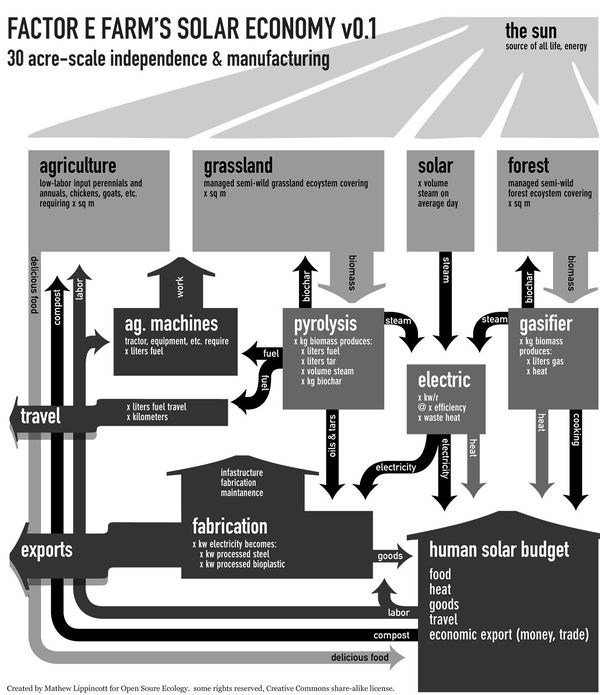
Note also: the materials ecology shown on this page should be compared to and integrated with the Solar Economy flow graphic [http://openfarmtech.org/w/images/c/c5/OSE_Trifold_Design_1_front.jpg here] | Note also: the materials ecology shown on this page should be compared to and integrated with the Solar Economy flow graphic [http://openfarmtech.org/w/images/c/c5/OSE_Trifold_Design_1_front.jpg here] | ||
The bulk of these product ecology diagrams were drawing using MS PowerPoint. See [[File:OSE-Product-Ecologies.ppt]] | |||
== Product Ecologies == | == Product Ecologies == | ||
There | There are a number of product ecologies that can be drawn up:<br> | ||
{| style="width:100%;" cellpadding="3" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="left" | {| style="width:100%;" cellpadding="3" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="left" | ||
|-align="left" | |-align="left" | ||
Revision as of 01:26, 26 September 2011
see also: GVCS Pattern Language
Introduction
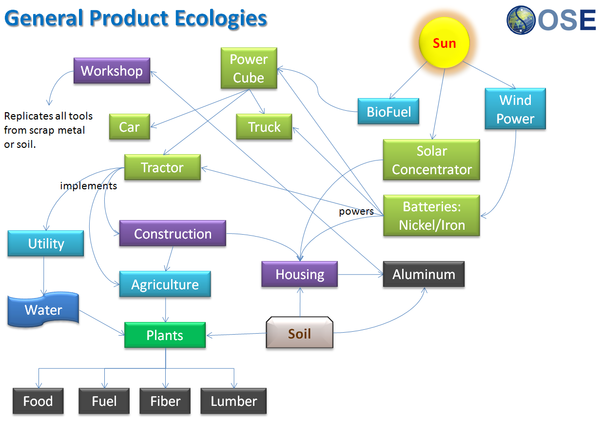
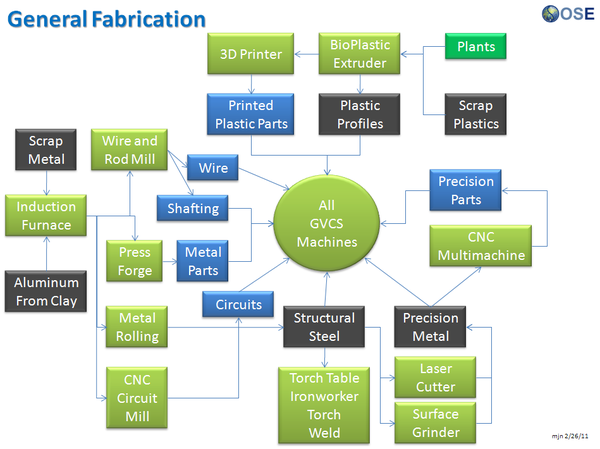
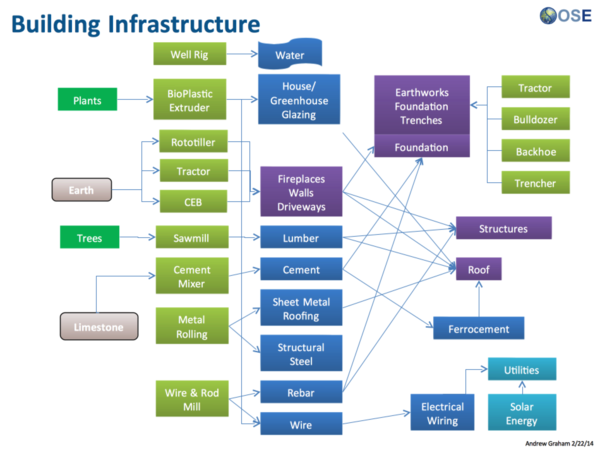
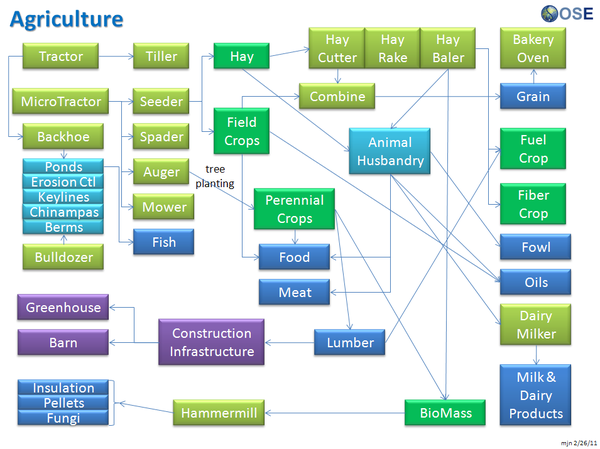
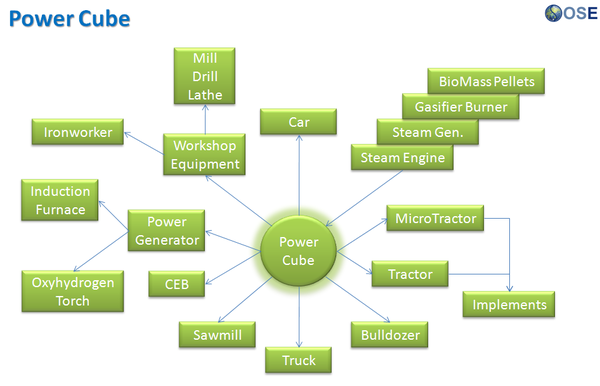
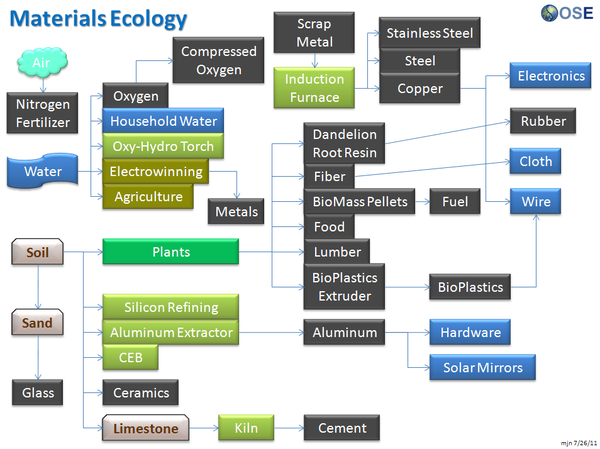
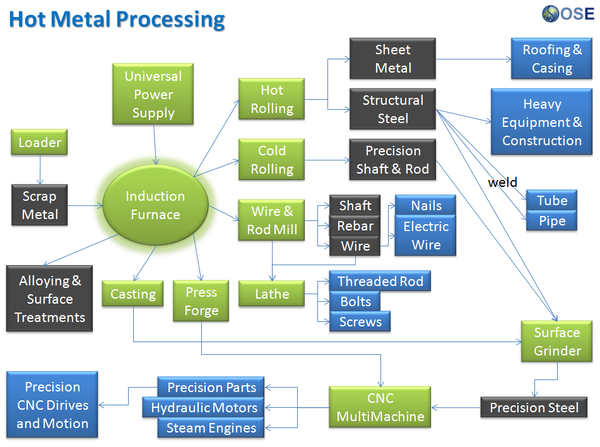
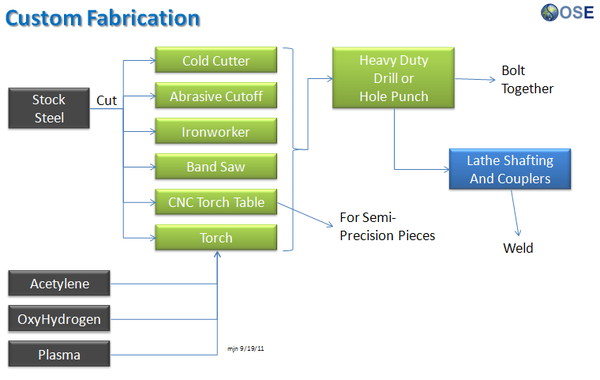
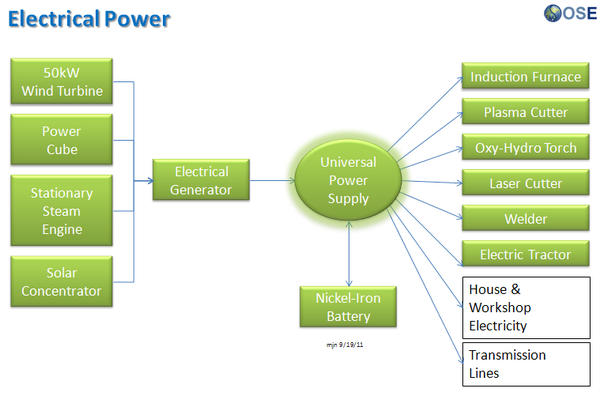
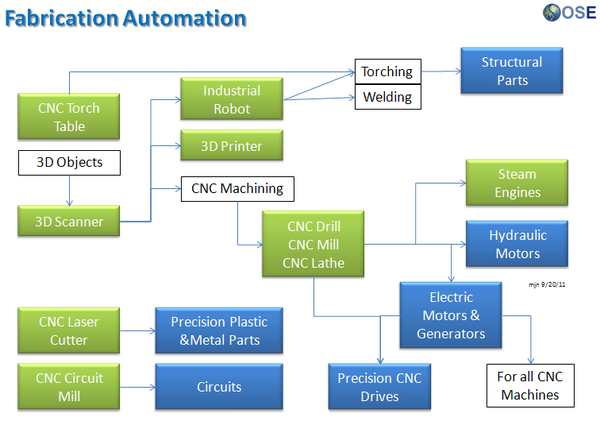
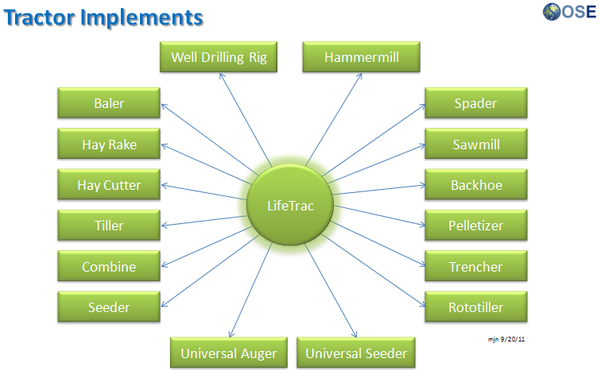
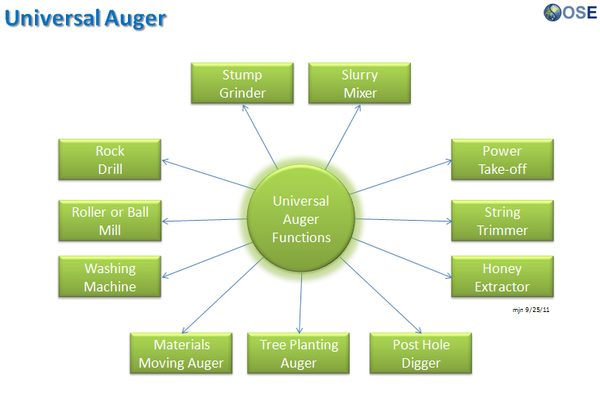
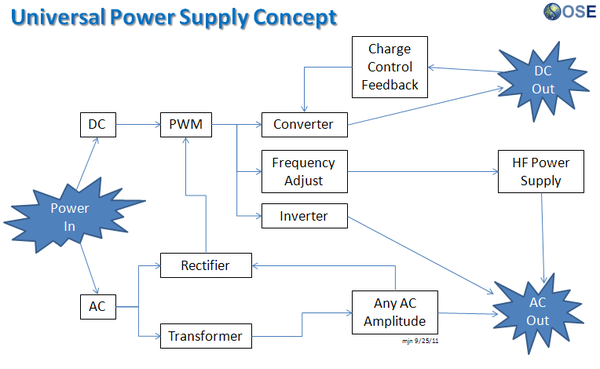
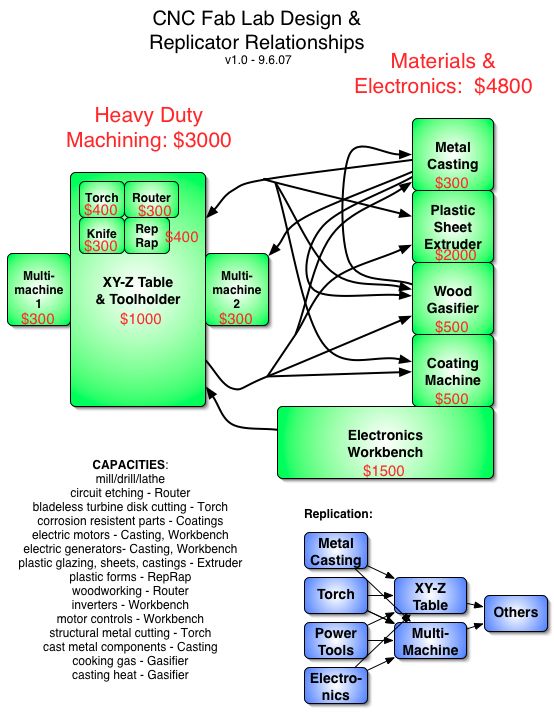
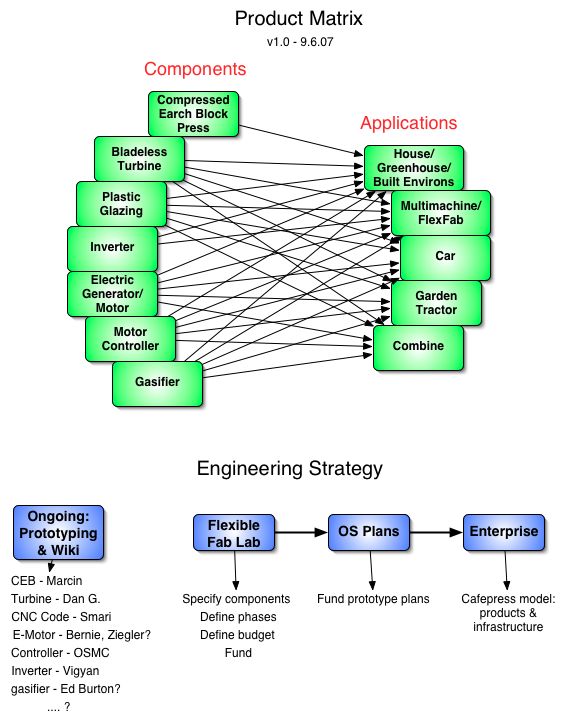
Product Ecologies illustrate how the different tools of the GVCS work together. For example, motors, power units, and implements interchange within the tractor, microtractor, car, truck, fabrication, and bulldozer infrastructures. Ecologies can also refer to the way in which a set of tools can be put together to produce a wide array of products - such as the induction furnace contributing to the production of tractor parts, construction roofing, or wire.
Note also: the materials ecology shown on this page should be compared to and integrated with the Solar Economy flow graphic here
The bulk of these product ecology diagrams were drawing using MS PowerPoint. See File:OSE-Product-Ecologies.ppt
Product Ecologies
There are a number of product ecologies that can be drawn up: