Hydraulic Motor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
|Enables= | |Enables= | ||
* {{Industrial Robot}} | * {{Industrial Robot}} | ||
* {{Plastic Extruder}} | * {{Plastic Extruder}} | ||
* {{Powercube}} | * {{Powercube}} | ||
* {{CEB Press}} | * {{CEB Press}} | ||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
* {{Car}} | * {{Car}} | ||
* {{Truck}} | * {{Truck}} | ||
* {{Power Cube}} | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 19:45, 29 September 2011
| Hydraulic Motor | ||
|---|---|---|
| Home | Research & Development | Bill of Materials | Manufacturing Instructions | User's Manual | User Reviews | 
| |
Overview
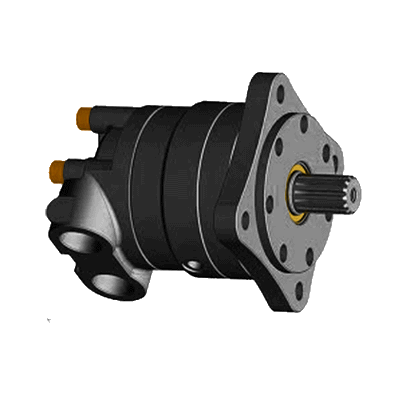
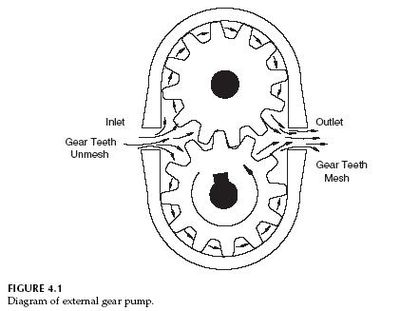
A hydraulic motor is a mechanical actuator that converts hydraulic pressure and flow into torque and rotation.
Detailed Description
In the GVCS, the hydraulic motor forms the energy backbone powering much of the equipment. Hydraulic power offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive aspect in helping machine meet OSE Spec
See Power Cube, CEB, and Tractor for implementation examples.
Product Ecology
| From | Uses | Creates | Enables |
|---|---|---|---|
Components |
|
Components
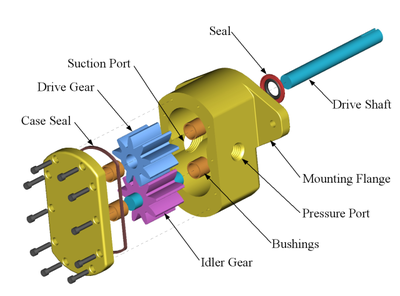
- Gears
- Casing
- Bearings
- Bushings
- Shaft
- Seal
Status
The Hydraulic Motor is currently in the research phases and is dependant on product release of precision equipment provided by Multimachine.
See Also