Microcombine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
*[[Microcombine/Research_Development|Research]] | *[[Microcombine/Research_Development|Research]] | ||
*[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combine_harvester Combine Harvester] | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combine_harvester Wikipedia: Combine Harvester] | ||
*[[Combine Research Paper]] | |||
{{GVCS_List}} | {{GVCS_List}} | ||
Revision as of 08:09, 5 September 2011
| Microcombine | ||
|---|---|---|
| Home | Research & Development | Bill of Materials | Manufacturing Instructions | User's Manual | User Reviews | 
| |
Overview
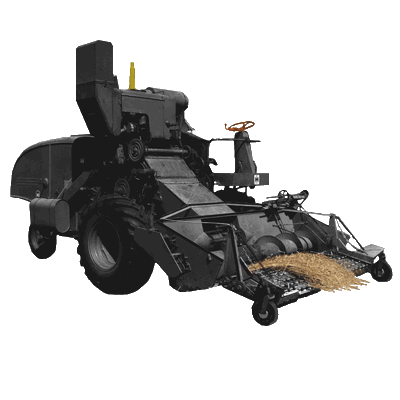
Agricultural Microcombine (Combine) - a combine is a complex device that cuts, threshes, and winnows grains and field crops of all sorts.
Details
Modern combines are huge devices today, and a smaller one is desirable for a small farm. This is not to say that this design should not be scaleable to larger size, as required to feed larger populations effectively. We propose a hybrid combine, with all parts driven by separate, infinitely speed controllable motors. This eliminates all pulleys and complexity of a single power source powering the entire modern combine. The key here is availability of cost-effective motors and controls, where today, motor controls are prohibitively expensive for such a proposition. OS changes this. With a microcombine under the control of the operator, expensive maintenance is avoided, and full food sufficiency becomes feasible on the tens-of-acres scale.
Product Ecology
Uses
- Furnace - Steel
- Torch Table - Parts
- Power Cube - Power
- Multimachine - Precision Parts
- Hydraulic Motor - Movement
- Tractor - Mounting
Components
Status
Current work includes getting information from grain and bean farmers about their needs for a microcombine, the operation modes they'd like, etc. and surveying any commercial equipment available that is similar in scope/scale.
See Also