CEB Press: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
{{Video}} | {{Video}} | ||
== | ==Details== | ||
The [[CEB Press]] takes earth/dirt/soil and compresses it tightly to make solid blocks useful for building. Compressed earth blocks have many advantages as a building material: by making the building materials from the readily available dirt on the building site, they eliminate the need to transport bricks from elsewhere, reducing the financial cost and environmental impact of transport. Compressed earth blocks are very strong and insulate well against both heat and sound, making for very energy-efficient building (especially combined with the energy savings from not needing to transport them from offsite). Best of all, the material they use is already on-site and does not need to be purchased -- quite literally, dirt-cheap! See the wiki page on [[Compressed Earth Blocks]] and the [[:Category:CEB|CEB category]] for more details on building using CEBs. | The [[CEB Press]] takes earth/dirt/soil and compresses it tightly to make solid blocks useful for building. Compressed earth blocks have many advantages as a building material: by making the building materials from the readily available dirt on the building site, they eliminate the need to transport bricks from elsewhere, reducing the financial cost and environmental impact of transport. Compressed earth blocks are very strong and insulate well against both heat and sound, making for very energy-efficient building (especially combined with the energy savings from not needing to transport them from offsite). Best of all, the material they use is already on-site and does not need to be purchased -- quite literally, dirt-cheap! See the wiki page on [[Compressed Earth Blocks]] and the [[:Category:CEB|CEB category]] for more details on building using CEBs. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 17: | ||
Building a machine yourself might seem intimidating, but every step of the process is fully documented and the OSE community is available on our [http://openfarmtech.org/forum/ discussion forums] if you need help, advice, or a little hand-holding. | Building a machine yourself might seem intimidating, but every step of the process is fully documented and the OSE community is available on our [http://openfarmtech.org/forum/ discussion forums] if you need help, advice, or a little hand-holding. | ||
Using the | Using the CEB Press, two people can build a 6 foot high (1.83m) round wall, 20 feet (6.1m) in diameter, 1 foot (30cm) thick, in one 8 hour day, though construction time will vary somewhat depending on preparation time, what equipment is available (tractor to prepare the ground and move the blocks where they need to go), the quality of the soil, and other factors. The bigger the block size, the faster a wall can be erected, but at the cost of heavier blocks that are more of a strain to work with. Blocks from ''The Liberator'' average 25 pounds (11.3kg). | ||
see [[CEB Design]] for more information. | |||
==Product Ecology== | ==Product Ecology== | ||
[[Image:4b-Constructioneco.png|thumb|600px|Construction [[Product Ecology]]]] | [[Image:4b-Constructioneco.png|thumb|600px|Construction [[Product Ecology]]]] | ||
{{Product Ecology | |||
|Product={{CEB}} | |||
|From= | |||
*{{Furnace}} | |||
*{{Welder}} | |||
*{{Torch Table}} | |||
*{{Ironworker}} | |||
|Uses= | |||
*{{PowerCube}} | |||
*{{Tractor}} | |||
*{{ | *[[Earth]] | ||
*{{ | |||
* | |||
| | |Creates= | ||
*[[CEB Bricks]] | |||
| | |Enables= | ||
*[[Workshop]] | |||
*[[Greenhouse]] | |||
*[[HabLab]] | |||
==Status== | ==Status== | ||
[[Image:creationreplication.jpg|thumb|James Slades' first independent replication of the CEB Press in process as of Sep. 2, 2011. Welding the soil loading drawer.]] | [[Image:creationreplication.jpg|thumb|James Slades' first independent replication of the CEB Press in process as of Sep. 2, 2011. Welding the soil loading drawer.]] | ||
*Currently the CEB is at product release status and is being actively manufactured at Factor e Farm and in Texas. The presses will be used heavily as a part of the [[Factor e Farm Infrastructure Buildout 2011]]. | |||
*The CEB documentation is being actively upgraded to meet [[Fabrication_Procedure_Standards]] with the goal of serving as a reference implementation for [[GVCS]] documentation. | |||
Currently the CEB is at product release status and is being actively manufactured at Factor e Farm. The presses will be used heavily as a part of the [[Factor e Farm Infrastructure Buildout 2011]]. | *Eventually the [[CNC Torch Table|torch table]] will be used to automate the fabrication of the CEB machine, reducing fabrication time by an estimated 20 hours and, thus, the cost to build the machine. | ||
*The first independent replication is in process as of Sep. 2, 2011, by [[James Slade]] and Jason Smith in Texas. | |||
The CEB documentation is being actively upgraded to meet [[Fabrication_Procedure_Standards]] with the goal of serving as a reference implementation for [[GVCS]] documentation. | |||
The first independent replication is in process as of Sep. 2, 2011, by [[James Slade]] and Jason Smith in Texas. | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[CEB Design]] | |||
*[[Compressed Earth Blocks]] | *[[Compressed Earth Blocks]] | ||
*[[Cinva Ram]] | *[[Cinva Ram]] | ||
{{GVCS Footer}} | {{GVCS Footer}} | ||
Revision as of 05:10, 1 October 2011
| CEB Press | ||
|---|---|---|
| Home | Research & Development | Bill of Materials | Manufacturing Instructions | User's Manual | User Reviews | 
| |
Overview

The "Liberator" Compressed Earth Block Press is a machine that makes compressed earth blocks (CEBs).
Details
The CEB Press takes earth/dirt/soil and compresses it tightly to make solid blocks useful for building. Compressed earth blocks have many advantages as a building material: by making the building materials from the readily available dirt on the building site, they eliminate the need to transport bricks from elsewhere, reducing the financial cost and environmental impact of transport. Compressed earth blocks are very strong and insulate well against both heat and sound, making for very energy-efficient building (especially combined with the energy savings from not needing to transport them from offsite). Best of all, the material they use is already on-site and does not need to be purchased -- quite literally, dirt-cheap! See the wiki page on Compressed Earth Blocks and the CEB category for more details on building using CEBs.
The Liberator has been fully designed and tested by the Open Source Ecology team. Because the Liberator is an open source technology, you can freely download instructions to build your own from materials you can obtain yourself, or contact opensourceecology[at]gmail[dot]com to buy a kit or a finished machine.
Building a machine yourself might seem intimidating, but every step of the process is fully documented and the OSE community is available on our discussion forums if you need help, advice, or a little hand-holding.
Using the CEB Press, two people can build a 6 foot high (1.83m) round wall, 20 feet (6.1m) in diameter, 1 foot (30cm) thick, in one 8 hour day, though construction time will vary somewhat depending on preparation time, what equipment is available (tractor to prepare the ground and move the blocks where they need to go), the quality of the soil, and other factors. The bigger the block size, the faster a wall can be erected, but at the cost of heavier blocks that are more of a strain to work with. Blocks from The Liberator average 25 pounds (11.3kg).
see CEB Design for more information.
Product Ecology
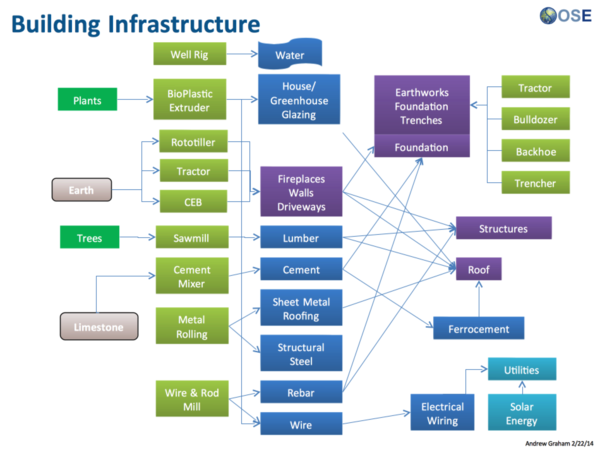
{{Product Ecology
|Product= CEB Press
|From=
CEB Press
|From=
|Uses=
|Creates=
|Enables=
Status
- Currently the CEB is at product release status and is being actively manufactured at Factor e Farm and in Texas. The presses will be used heavily as a part of the Factor e Farm Infrastructure Buildout 2011.
- The CEB documentation is being actively upgraded to meet Fabrication_Procedure_Standards with the goal of serving as a reference implementation for GVCS documentation.
- Eventually the torch table will be used to automate the fabrication of the CEB machine, reducing fabrication time by an estimated 20 hours and, thus, the cost to build the machine.
- The first independent replication is in process as of Sep. 2, 2011, by James Slade and Jason Smith in Texas.
See Also







