Laser Cutter: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
==Components== | ==Components== | ||
*[[Laser]] | *[[Laser]] | ||
*[[ | *[[XYZ Table]] | ||
*[[Controller]] | *[[Controller]] | ||
Revision as of 02:54, 20 September 2011
| Laser Cutter | ||
|---|---|---|
| Home | Research & Development | Bill of Materials | Manufacturing Instructions | User's Manual | User Reviews | 
| |
Overview
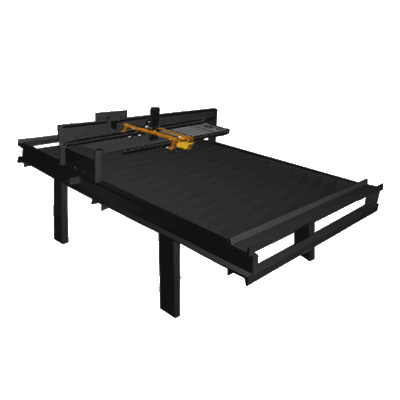
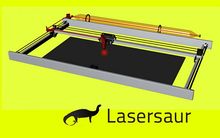
A laser cutter enables CNC cutting and engraving of metal, wood, and other materials. Laser cutting works by directing the output of a high-power laser, by computer, at the material to be cut. The material then either melts, burns, vaporizes away, or is blown away by a jet of gas, leaving an edge with a high-quality surface finish. Industrial laser cutters are used to cut flat-sheet material as well as structural and piping materials.
Details
lasersaur from stefanix on Vimeo.
Product Ecology
Uses
- Induction Furnace - Structural Metal
- Multimachine -
- CNC Circuit Mill - Controller
- Motors
- Power
Creates
- 3D Printer - Structural
Components
See Product Ecologies for more information.
Status
The Laser Cutter is currently in the Development phase by Lasersaur, and will be a part of the GVCS when complete.
Research
See Also