Gasifier Burner: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Details== | ==Details== | ||
This is achieved by reacting the material at high temperatures (>700°C), without combustion, with a controlled amount of oxygen and/or steam, breaking down the biomass into carbon monoxide, hydrogen, carbon dioxide and methane. The resulting gas mixture is a fuel called [[syngas]]. | This is achieved by reacting the material at high temperatures (>700°C), without combustion, with a controlled amount of oxygen and/or steam, breaking down the biomass into carbon monoxide, hydrogen, carbon dioxide and methane. The resulting gas mixture is a fuel called [[syngas]]. If Air is used in place of oxygen the gas also contains inert nitrogen and is called producer gas. | ||
==Product Ecology== | ==Product Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 01:55, 1 January 2012
| Gasifier Burner | ||
|---|---|---|
| Home | Research & Development | Bill of Materials | Manufacturing Instructions | User's Manual | User Reviews | 
| |
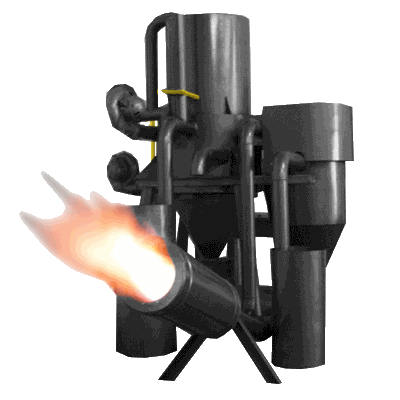
Overview
The Gasifier Burner converts biomass fuel into power and useful chemicals.
Details
This is achieved by reacting the material at high temperatures (>700°C), without combustion, with a controlled amount of oxygen and/or steam, breaking down the biomass into carbon monoxide, hydrogen, carbon dioxide and methane. The resulting gas mixture is a fuel called syngas. If Air is used in place of oxygen the gas also contains inert nitrogen and is called producer gas.
Product Ecology
| From | Uses | Creates | Enables |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Components
|
Status
The gasifier burner is currently in the Research phase of development.
See Also
- Biochemicals from Pyrolysis
- Biomass to FuelFischer-Tropsch
- Compressed Fuel Gas
- Pyrolysis Oil
- Biochar
- Babington Burner