Universal Power Supply: Difference between revisions
Graham12357 (talk | contribs) m (→Rectifyers) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{OrigLang}} | |||
{{GVCS Header}} | {{GVCS Header}} | ||
| Line 5: | Line 7: | ||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
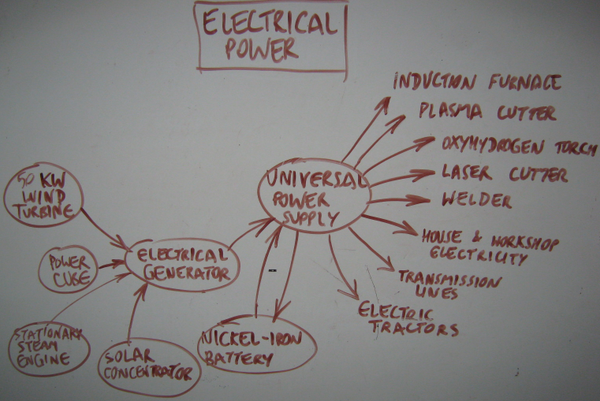
A Universal Power Supply forms the backbone of an [[off-grid]] electrical system. | A Universal Power Supply forms the backbone of an [[off-grid]] electrical system for powering machines and power electronic devices such as the induction furnace. | ||
=Updates= | |||
*See [[Universal_Power_Supply Requirement]] for 2019 version. | |||
*Initial prototypes: | |||
<html><iframe src="https://www.facebook.com/plugins/post.php?href=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.facebook.com%2Fmarcin.jakubowski.378%2Fposts%2F10216586886961796&width=500" width="500" height="529" style="border:none;overflow:hidden" scrolling="no" frameborder="0" allowTransparency="true" allow="encrypted-media"></iframe></html> | |||
{{Video}} | {{Video}} | ||
| Line 15: | Line 22: | ||
===Rectifiers=== | ===Rectifiers=== | ||
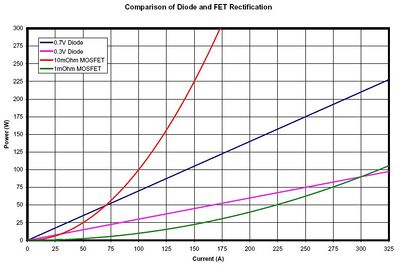
[[Image:FET_Diode_Comparison_Chart.JPG|400px|thumb| | [[Image:FET_Diode_Comparison_Chart.JPG|400px|thumb|Rectifier power dissipation as a function of current]] | ||
Rectification is the conversion of AC to DC. A universal power supply would require one or two rectifying stages: one at the AC input to provide DC for the voltage converter, and another if the voltage converter is a proper Active PFC converter, which produces PWM shaped output. | Rectification is the conversion of AC to DC. A universal power supply would require one or two rectifying stages: one at the AC input to provide DC for the voltage converter, and another if the voltage converter is a proper Active PFC converter, which produces PWM shaped output. | ||
| Line 66: | Line 73: | ||
=Status= | =Status= | ||
OSE is recruiting [[subject matter experts]] with experience in [[inverter]] design. Those with relevant experience are encouraged to [[Contact Us]] | OSE is recruiting [[subject matter experts]] with experience in [[inverter]] design. Those with relevant experience are encouraged to [[Contact Us]] | ||
[https://wiki.opensourceecology.org/wiki/Adjustable_Power_Supply_v18.08 Adjustable Power Supply v18.08 is in development] | |||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
| Line 74: | Line 83: | ||
*[[Problem Statement for a Universal Power Supply|Problem Statement]] | *[[Problem Statement for a Universal Power Supply|Problem Statement]] | ||
*[[Power Electronics Construction Set]] | *[[Power Electronics Construction Set]] | ||
*http://preciodelorohoy.wordpress.com/ - Information about power supply | |||
Latest revision as of 20:37, 30 October 2019
| Universal Power Supply | ||
|---|---|---|
| Home | Research & Development | Bill of Materials | Manufacturing Instructions | User's Manual | User Reviews | 
| |
Main > Energy > Power quality
Overview
A Universal Power Supply forms the backbone of an off-grid electrical system for powering machines and power electronic devices such as the induction furnace.
Updates
- See Universal_Power_Supply Requirement for 2019 version.
- Initial prototypes:
Definition/Concept
This is a combination inverter, converter, pulse-width modulation current controller, and high frequency power supply for applications from off-grid power, charge controllers, to power supplies for welders, induction furnaces, and plasma cutters.
A large range of power electronic devices is desirable within the infrastructure of communities. Having an individual power supply for each is redundant and expensive. A modular UPS construction kit is desirable as an analogue to the 'industrial-strength Lego' that we have already demonstrated for heavy mechanical hardware infrastructures.
Rectifiers
Rectification is the conversion of AC to DC. A universal power supply would require one or two rectifying stages: one at the AC input to provide DC for the voltage converter, and another if the voltage converter is a proper Active PFC converter, which produces PWM shaped output.
Rectifiers can be either passive schottky diode bridges, or active (IC-controlled) MOSFET H-bridges. Passive ones are cheaper, and ultimately more efficient for very high currents, while active ones are superior for low-medium-and-maybe-high currents yet more expensive. This design choice affects price, producability and simplicity.
In either case a rectifier stage requires power packaged components and a heat sink. The size of the heat sink is a function of the current, which is higher at low voltages for a given output power. Questions for the specification is how much power the device should be able to deliver from a 12V source (first rectifier in the case of voltage up-conversion) and to a load at 12V DC output (second rectifier if present).
Voltage Converters
Inverters
An inverter is an electrical device that converts DC voltage from batteries to AC voltage for off-shelf electrical tools and appliances.
Off-the-shelf inverters have about a 2 year lifetime, and 5-10 year lifetime for higher quality models. Lifetime design inverters with plug-in replacement components are required for sustainable communities which use battery storage as a component of their electricity infrastructure. One of the few other feasible, non-battery, non-fuel energy storage may be via heat storage coupled to thermoelectric generators, or possibly thermal storage via phase-change salts and heat engines.
Product Ecology
| From | Uses | Creates | Enables |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Components |
Status
OSE is recruiting subject matter experts with experience in inverter design. Those with relevant experience are encouraged to Contact Us
Adjustable Power Supply v18.08 is in development
See Also
- Concept
- Inverter
- Electricity
- Charge Controller
- Problem Statement
- Power Electronics Construction Set
- http://preciodelorohoy.wordpress.com/ - Information about power supply