Bioplastic Extruder/Research Development: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
[[Image:BioPlasticExtruder.jpg|thumb|400px|Bioplastic Extruder Diagram]] | |||
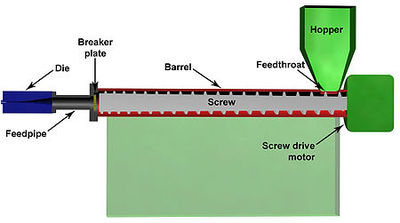
[[Image:BioPlasticExtruderDetail.jpg|thumb|400px|Detail]] | |||
==Bioplastics== | ==Bioplastics== | ||
Revision as of 18:16, 19 September 2011
| Bioplastic Extruder | ||
|---|---|---|
| Home | Research & Development | Bill of Materials | Manufacturing Instructions | User's Manual | User Reviews | 
| |
Overview
Bioplastics
Cellophane is reformulated cellulose (wood), produced via an acid and base dunk of sawdust. This may be used in glazing. Car bodies may be made; the original car bodies for Ford were soybean-derived bioplastics.
Polylactic acid (PLA) can be made by fermenting starch or with hay in silage.
Mycelium can be placed in a mold with grain husks, wheat straw or any of a wide variety of other biomass (with different end product results) and be made into a variety of useful products, including a durable closed cell foam substitute.
Links
- plastics extrusion
- Wikipedia: Plastics Extrusion
- Wikipedia: Thermoforming
- Wikipedia: Vacuum Forming
- Wikipedia: Injection Molding
- Strictly Extrusion
- Society of Plastics Engineers
- SPE Online Technical Library
See Also
- Waste Plastic Extruder: Literature Review
- Bioplastics
- Plastic Extrusion & Molding
- Upper Austria Green Biorefinery
- Polyethylene from Ethanol