Power Cube/Manufacturing Instructions: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Tom Griffing (talk | contribs) |
m (Fixed link) |
||
| (293 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{GVCS Header}} | ||
{{Power_Cube_Manufacturing_Instructions_Navbox}} | {{Power_Cube_Manufacturing_Instructions_Navbox}} | ||
<br /> | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
<html><iframe src="https://player.vimeo.com/video/29562529?title=0&byline=0&portrait=0" width="500" height="300" frameborder="0" webkitAllowFullScreen allowFullScreen></iframe></iframe></html> | |||
[[Image:Powercube4.jpg|thumb]] | |||
<br /> | |||
[[Power Cube/Intro Video Script | Intro to Power Cube Construction Script]] | |||
==Preparation== | |||
# [[PowerCube_Safety|Safety]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Workspace|Workspace]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Tools|Tools]] | |||
==Subassembly Fabrication== | ==Subassembly Fabrication== | ||
The purpose of this section is to cut the raw steel into required lengths and shapes as required for final assembly. These step includes drilling and cutting steel up to 3/8” in thickness. | |||
# [[PowerCube_Engine & Hydraulic Pump mounts|Engine & Hydraulic Pump mounts]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Quick attach mounts|Quick attach mounts]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Fuel tank|Fuel tank]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Oil Cooler Mount|Oil Cooler Mount]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Key Switches and Choke|Key Switches and Choke]] | |||
[[ | # [[PowerCube_Electrical cables|Electrical cables]] | ||
# [[PowerCube_Battery Mount|Battery Mount]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Mufflers|Mufflers]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Hydraulic reservoir|Hydraulic reservoir]] | |||
==== | ==Assembly== | ||
Power Cube assembly requires all the parts listed in the Bill Of Materials to be available and prepared as detailed in the “Fabrication” section (above). Assembly requires a welder (electric or torch) capable of welding metal 3/8” thick. | Power Cube assembly requires all the parts listed in the Bill Of Materials to be available and prepared as detailed in the “Fabrication” section (above). Assembly requires a welder (electric or torch) capable of welding metal 3/8” thick. | ||
A [[Power Cube Jig]] can be very useful during the welding stage | A [[Power Cube Jig]] can be very useful during the welding stage: | ||
::[[Image:Pcframeweld.jpg|thumb|Power Cube Frames welding - 45 minutes per frame with one person assisting on jig clamping.]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Frame|Frame]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Gas tank|Gas tank]] | |||
[[ | # [[PowerCube_Hydraulic tank|Hydraulic tank]] | ||
# [[PowerCube_Engine Mounts and Hydraulic Motor Mount|Engine and Hydraulic Motor Mount]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Battery mount|Battery mount]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Oil cooler and fan mounts|Oil cooler and fan mounts]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Solenoid Mounting Bolts|Solenoid Mounting Bolts]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_ThrottleSwitchMounts|Keyswitch and Throttle mounts]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Quick Attach Plates|Quick Attach Plates]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Finish and Painting|Finish and Painting]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Install Hydraulic Components|Install Hydraulic Components]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_InstallEnginePump|Install Engine and Hydraulic Pump]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Install Solenoid|Install Solenoid]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Install Mufflers|Install Mufflers]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Wiring|Wiring]] | |||
# [[PowerCube_Throttle|Install Throttle Control]] | |||
==== | ==Final touches== | ||
# Install engine and secure with bolts, nuts and washers | |||
# Connect wiring to key switch and solenoid | |||
# Connect fuel line | |||
# Connect coupling to engine shaft | |||
# Install hydraulic pump on coupling and secure with nuts & washers | |||
# Install fan and hydraulic oil cooler | |||
==See Also== | |||
See also [[Power_Cube_Fabrication_Procedure]] for older model. | See also [[Power_Cube_Fabrication_Procedure]] for older model. | ||
Work in progress by Tom Griffing - [[File:powercube.odt]] | Work in progress by Tom Griffing - [[File:powercube.odt]][[File:powercube.pdf]] | ||
[[Image:PowerCube.skp|PowerCube Sketchup Drawing]] | |||
==Previous Versions== | ==Previous Versions== | ||
[[Power Cube/Manufacturing Instructions/Fabrication June 2011|Power Cube Fabrication June 2011]] | [[Power Cube/Manufacturing Instructions/Fabrication June 2011|Power Cube Fabrication June 2011]] | ||
{{GVCS Footer}} | |||
Latest revision as of 13:02, 6 January 2012
| Power Cube | ||
|---|---|---|
| Home | Research & Development | Bill of Materials | Manufacturing Instructions | User's Manual | User Reviews | 
| |
| |||||||||||
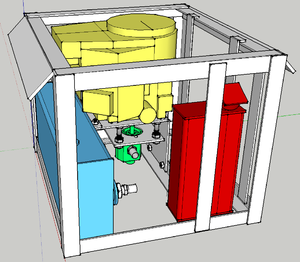
Overview
Intro to Power Cube Construction Script
Preparation
Subassembly Fabrication
The purpose of this section is to cut the raw steel into required lengths and shapes as required for final assembly. These step includes drilling and cutting steel up to 3/8” in thickness.
- Engine & Hydraulic Pump mounts
- Quick attach mounts
- Fuel tank
- Oil Cooler Mount
- Key Switches and Choke
- Electrical cables
- Battery Mount
- Mufflers
- Hydraulic reservoir
Assembly
Power Cube assembly requires all the parts listed in the Bill Of Materials to be available and prepared as detailed in the “Fabrication” section (above). Assembly requires a welder (electric or torch) capable of welding metal 3/8” thick.
A Power Cube Jig can be very useful during the welding stage:
- Frame
- Gas tank
- Hydraulic tank
- Engine and Hydraulic Motor Mount
- Battery mount
- Oil cooler and fan mounts
- Solenoid Mounting Bolts
- Keyswitch and Throttle mounts
- Quick Attach Plates
- Finish and Painting
- Install Hydraulic Components
- Install Engine and Hydraulic Pump
- Install Solenoid
- Install Mufflers
- Wiring
- Install Throttle Control
Final touches
- Install engine and secure with bolts, nuts and washers
- Connect wiring to key switch and solenoid
- Connect fuel line
- Connect coupling to engine shaft
- Install hydraulic pump on coupling and secure with nuts & washers
- Install fan and hydraulic oil cooler
See Also
See also Power_Cube_Fabrication_Procedure for older model.
Work in progress by Tom Griffing - File:Powercube.odtFile:Powercube.pdf
Previous Versions
Power Cube Fabrication June 2011